Many people may be aware that diabetes affects your body. But did you know it can also affect ocular health?
If you have diabetes, it’s essential to care for your eyes because diabetes can affect your vision over time, commonly known as diabetic eye disease. That’s where a diabetic eye exam comes in.
A diabetic eye exam is a comprehensive eye exam that checks for damage or changes in the eyes caused by diabetes. Usually conducted by your optometrist or ophthalmologist, this exam can thoroughly examine the retina (the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye) and blood vessels in your eyes.
What Is Diabetes & How Does it Affect Your Eyes?
Diabetes is a chronic condition where your body can’t properly process glucose, a type of sugar that provides energy to your body. Insulin is a hormone that regulates your blood sugar levels.
But when your pancreas doesn’t produce enough insulin or your body doesn’t respond to the insulin produced, it can lead to excess sugar in the blood. When your blood sugar levels are high and uncontrolled, it can cause damage to the blood vessels throughout your body, including the blood vessels in your eyes.
Eye Conditions Linked to Diabetes
Diabetic retinopathy is the most common eye complication associated with diabetes. It occurs when high blood sugar levels cause damage to the tiny blood vessels that nourish the retina.
As a result, the blood vessels may leak blood or fluid into the retina or close off altogether to block blood flow. If blood flow diminishes, new blood vessels can grow (neovascularization), but they may be abnormal and leak or rupture.
Diabetic retinopathy can lead to vision loss or even blindness if the damage worsens. It’s important to note that diabetic retinopathy often has no early warning signs or symptoms, so it’s crucial to have regular eye exams to detect damage before it gets worse or causes vision loss.
As the disease progresses, symptoms of diabetic retinopathy can include:
- Floaters, which are dots or dark strings in your field of vision
- Dark spots or empty areas in your field of vision
- Blurry vision
- Difficulty focusing
- Fluctuating vision changes
- Altered colour vision
- Partial or total vision loss
Diabetes can increase your risk of other eye problems, such as:
- Cataracts: Occurs when the lens of the eye becomes cloudy. If you have diabetes, you are 2 to 5 times more likely to get cataracts.
- Glaucoma: Occurs when the optic nerve gets damaged. If you have diabetes, it nearly doubles your risk of developing open-angle glaucoma.
Diabetic macula edema is a complication of diabetic retinopathy caused when blood vessels leak into the macula (a part of your eye that controls central vision) and results in swelling. A swollen macula can cause irreversible central vision loss.
It’s crucial to manage your blood sugar levels if you have diabetes and have regular eye exams. By taking care of your health and managing your diabetes, you can reduce your risk of eye complications and other eye diseases.
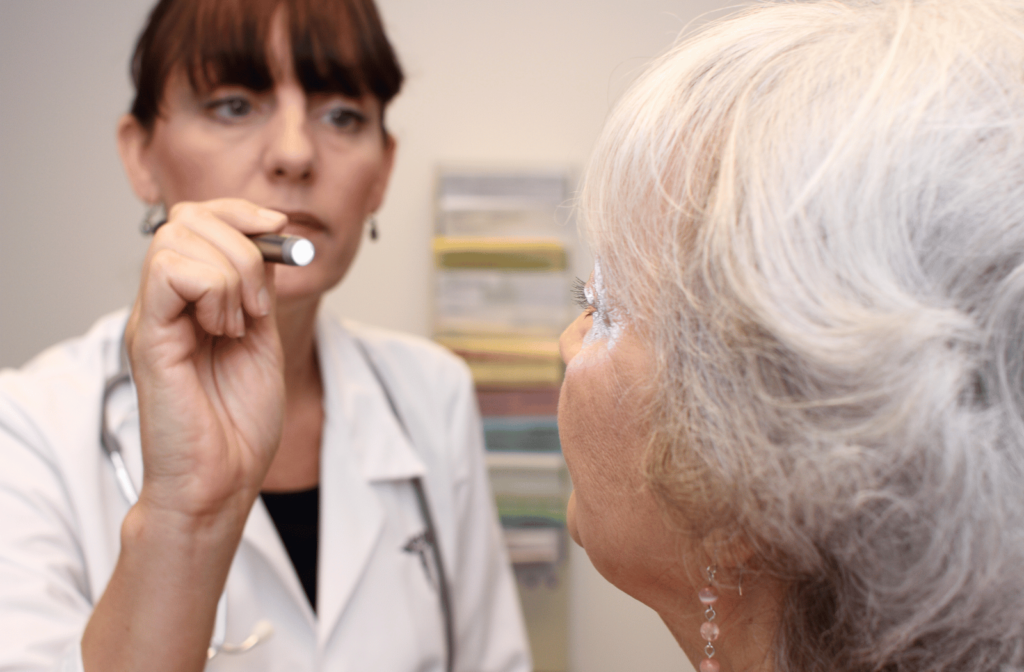

A Diabetic Eye Exam Explained
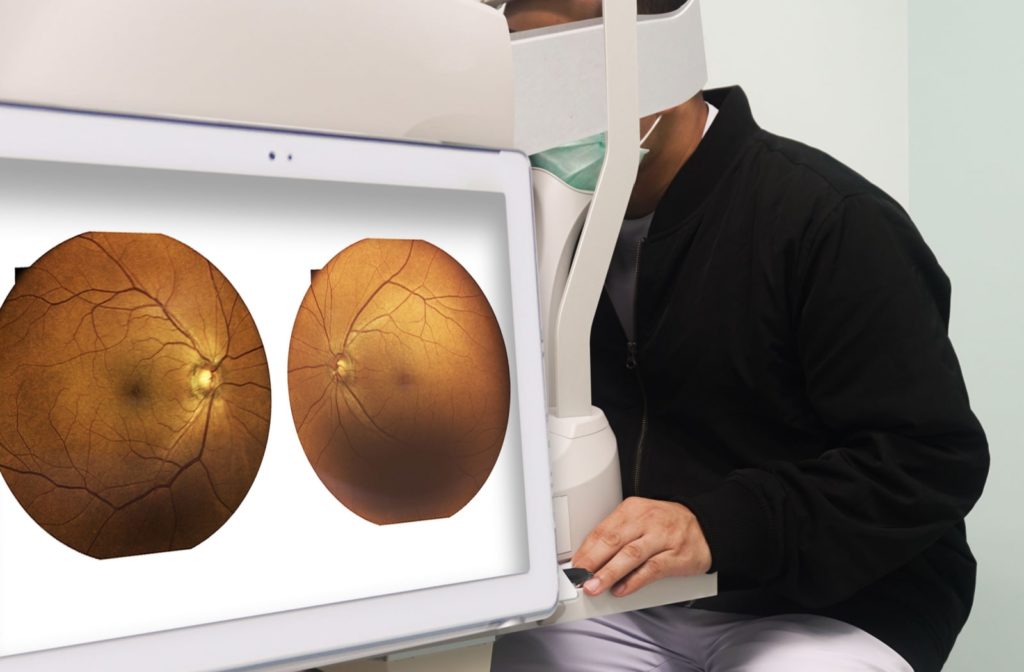
An eye exam can detect diabetes in its early stages. But a diabetic exam that includes dilation is the only way to diagnose diabetic retinopathy. During the exam, your eye doctor can dilate your pupils to examine the inside of your eyes with diagnostic tests to look for damage.
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
OCT provides images of your eyes that allow your eye doctor to see fine details, such as the thickness of your retina and fluid leakage from damaged blood vessels.
Fluorescein Angiography
During dilation, your doctor uses a special dye to take pictures of the inside of your eyes. This allows them to see which blood vessels are damaged, have blockages, and which vessels leak blood.
How Often Should You Have a Diabetic Eye Exam
By having regular eye exams, you can catch any eye problems early and prevent them from getting worse. For patients with diabetes, the recommendation is to have an eye exam at least once a year or more often if directed by your eye doctor.
For patients with diabetic retinopathy, regular eye exams help monitor changes in your eyes. These may include several exams per year and can depend on the treatment and severity of the retinopathy.
Treatment for diabetic retinopathy aims to slow or stop the progression. Treatment options can include:
- Controlling blood sugar levels
- Laser treatment to stop leakage or shrink abnormal blood vessels
- Vitrectomy to remove leaked blood
- Vision correction, such as glasses or contact lenses
Preventing Vision Loss with Eye Exams
Taking care of your eyes is essential for managing your diabetes, staying healthy, and protecting your vision. If you have diabetes, don’t delay scheduling a diabetic eye exam with Eye Effects in Calgary and Didsbury.